How Hands-On Coding Can Benefit Future Computer Science Teachers
Chanel Belvin, Elaine Anita De Melo Gomes Soares, Toni Dunlap, James Newland
Expanding Pathways in Computing,
Texas Advanced Computing Center,
University of Texas at Austin
Introduction
- To broaden participation in computing (BPC), we need more high-quality, certified Computer Science (CS) teachers to help build the high-performance computing pipeline (HPC).
- Teacher certification exams focus heavily on abstract pseudocode, which is disconnected from the practical, hands-on coding skills needed for effective classroom teaching.
- We’ve observed that pseudocode skill alone is insufficient. Teachers struggle with the exam and lack the confidence to teach programming concepts.
- How can we adjust teacher training to bridge the gap between theory and practice, building both confidence and competence?
Previous Training Model
Live Python Sessions
- Synchronous, live instruction using CMU CS Academy.
- Builds practical, hands-on programming skills.
Exam-Specific Training
- Targeted course on exam-style pseudocode.
- Self-paced “Foundations of CS” course with videos and practice covering all exam topics.
In-Person Cert Prep & Practice Tools
- A dynamic two-day, in-person certification workshop.
- Final practice packet with additional review tools before the exam.
- Focused on interpreting and using pseudocode in context.
- Many practice questions employ multiple pseudocode components such as loops, arrays, conditionals, and data types.


Improved Training Model
Positive Impact of Live Coding
- The addition of live coding experiences in the CS learning process positively impacts learners.2
Foundational Learning
- We now begin with a “Pseudocode Bootcamp” to teach coding concepts directly within the exam’s format.
- This allows for more extensive time on foundational principles before introducing a specific programming language.
Strengthened Cohort Model
- A new in-person orientation builds strong peer-to-peer support networks from the very beginning.
- Each cohort is guided by a dedicated instructional leader who shares best practices and resources.
Teacher Readiness & Support
- Practical programming language training is now offered after certification to focus specifically on classroom readiness.
- For teachers needing a retake, we offer “Domain Nights,” gamified review sessions that target specific areas for improvement.

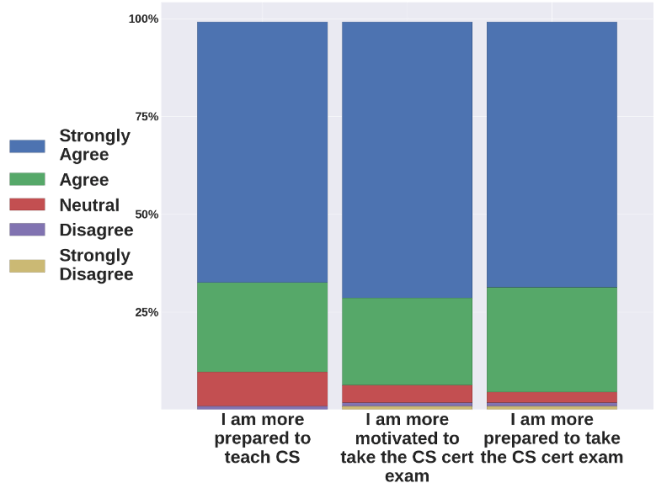
Participant Feedback

Future Research
- Analysis of the role of pseudocode in teacher attitudes and self-efficacy.
- Report on the effect of certification exam use of mathematical thinking on teacher success.
- Evaluation of the former training model versus the improved training model.
References
- 1Saupp, B., Macmillan, E., Mayfield, C., Johnson, C., Stewart, M. C., & Hodges, S. (2025). Praxly: An Online IDE for the Praxis CS Test Pseudocode. SIGCSE TS 2025 – Proceedings of the 56th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education, 2, 1613–1614. https://doi.org/10.1145/3641555.3705231
- 2Raj, A. G. S., Patel, J. M., Halverson, R., & Halverson, E. R. (2018, November 12). Role of live-coding in learning introductory programming. ACM International Conference Proceeding Series. https://doi.org/10.1145/3279720.3279725